- August 23rd, 2025
Understanding Hepatitis B: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening viral infection that attacks the liver, causing inflammation and, in some cases, serious liver damage. W...
Read More
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening viral infection that attacks the liver, causing inflammation and, in some cases, serious liver damage. W...
Read More
Back pain is one of the most common health complaints people face worldwide. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or lifestyle, and it can vary fro...
Read More
Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune condition that affects millions worldwide, often going undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. At Siddhanta Superspecialit...
Read More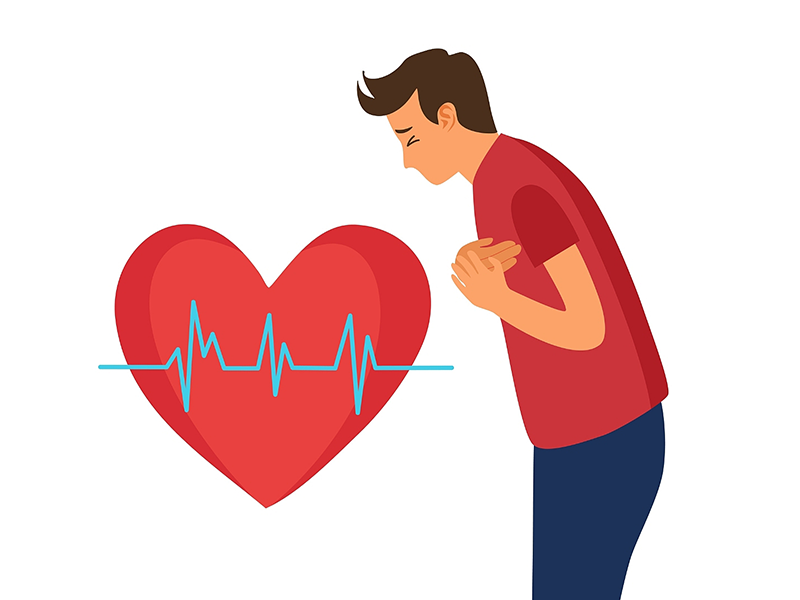
Heart health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and many people are familiar with terms like heart attack and heart failure. While both condi...
Read More
Understanding Osteoporosis: A Silent Threat to Bone Health Osteoporosis, often referred to as a "silent disease," is a condition characterized by wea...
Read MoreAll Copyrights Reserved by Siddhanta Superspeciality Hospital | Design By MaMITs